Aquatic life, especially for human consumption, is a controlled process of farming marine animals. It is similar to agriculture but has the same concept of fish rather than plants or livestock. The seafood you find at your local grocery store labeled as potentially farmed fish. Aquaculture can occur worldwide, and it does: in coastal seawater, in freshwater lakes and rivers, and even on land in tanks.
What is Aquaculture?
Aquaculture is the process of raising, breeding, and harvesting aquatic species, animals, and plants in a controlled environment, such as oceans, lakes, rivers, lakes, and streams.
It is using for various purposes, including food production, endanger species populations, wild stock community growth, aquarium and fish cultures and habitat restoration. The aquarium is also known as fish farming.
70% of the world’s surface is covered by water. Humans have realized aquaculture importance as a tool. The area of water use as a resource in pacific east aquaculture, especially in food production instead of terrestrial land.

Types of Aquaculture
Here are the different types of cultural practices that are carrying out in each of these divisions depending on:
(1) Fish Farming
Fish farming is the most publicly renown type of aquaculture. This includes selective breeding of fish, in freshwater or seawater, intending to produce food sources of consumption.
Fish farming is highly utilizing as it allows for the fish production of cheap sources of protein. Besides, fish farming is easier to do than other farming types because the fish do not care. These need proper food and water conditions as well as temperature.
The process is also less soil-intensive because the size of the ponds require to grow fish species such as tilapia. It is much smaller than the space needed to develop the same amount of protein from beef cattle.
(2) Inland Pond Culture
Inland Pond Culture includes inland artificial lakes about 20 acres in size and about 6-8 feet deep. It is common to see an aerated system attached to the lake to introduce air into the ponds. This increases the supply of oxygen and reduces ice formation in winter.
More than 25% of freshwater fish are producing in constructed ponds in China. Almost all farmed catfish live in the United States grows in the inland ponds and lakes.
(3) Alga culture
Alga culture also named as Algae culture is a type of aquaculture associated with algae cultivation. Algae are microbial organisms that share the characteristics of animals and plants. They are sometimes as productive and effective as other microorganisms.
They also contain chlorophyll, making them green and photosynthesize like green plants.
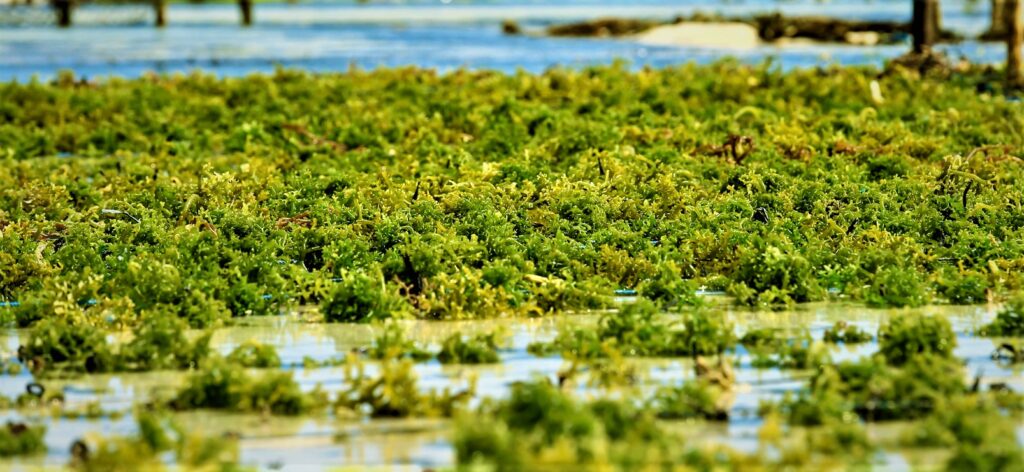

However, for economic viability, they are growing and cutting in large numbers. Algae are finding many applications in today’s markets. Exxon Mobile is moving to develop them as a new source of revenue.
(4) Mari culture
Marine aquaculture involves the use of seawater. It divided by the sea or in a lake separate from the sea, but the seawater is the same. Organisms raised here classify from molluscs to seafood alternatives such as prawns, shellfish, and seaweed.
Flowering plants like seaweed is also a part of Mari culture. These sea plant and animal species can find many uses in the manufacturing industries such as cosmetics and jewelry. Seaweeds are using to make facial creams. Pearls are taking from molluscs and made into fashion items.
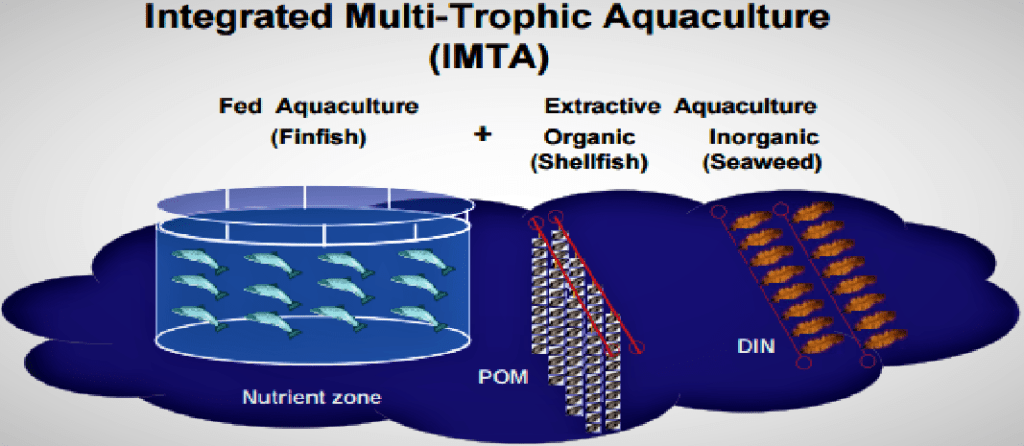
(5) Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture (IMTA)
IMTA is an advance aquaculture system where different trophic layers mixed into the system to meet each other’s nutritional needs. It is an efficient system as it attempts to simulate the ecological system that exists in the natural habitat.
IMTA uses the intertropical transfer of resources to ensure maximum resource utilization. It is using for large organism’s waste as a food source for small animals.
The multi-trophic system ensures that nutrients are recycling. It means the process is less wasteful and produces more products.
(6) Recirculating Systems
It is an environmentally friendly system because very little new water introduced to replace the evaporating water.
This includes a closed set of units where the fish kept in one and the water treated in the other. It is highly dependent on the power supply. Water has constantly pumped through the fish chamber.
As water flows from the treatment chamber, the particulate matter filtered, and the air introduced. This closed system controls salinity, oxygen, temperature and anything that harms the fish.
Filter residues are also disposing of responsibly from aquaculture Minecraft.
(7) Flow-through / Raceway
Raceways are common for cultivating trout. Flow-through is a system made up of long units filled with fish. Raceway units connected to the feeding stations. The water diverted from the running water and fed into the race-way units flowing downstream.
At the end of the unit, the waste is collecting and dispose of.
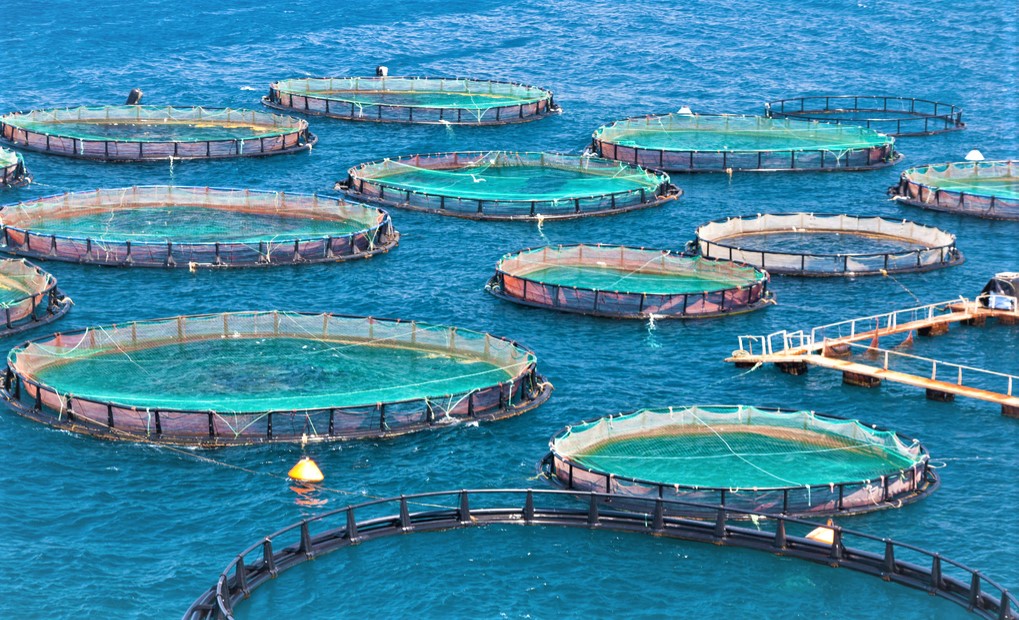
(8) Open-net Cage Systems
Cage systems with the open net often found in offshore and freshwater ponds. With a high concentration of fish in the pan, wastes, chemicals, parasites and diseases are frequently exchanging in an immediate aquatic environment. Mesh cages of 6 to 60 cubic feet are installed underwater.
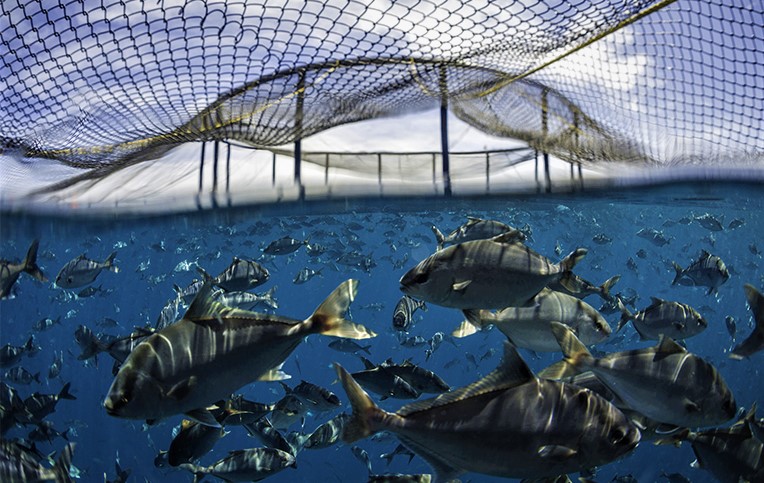

Fish also attract predators like large fish, which are often caught in nets. The system uses public water; therefore, environmental regulation and certain authorization protocols must be respected.
How Does Aquaculture Work?
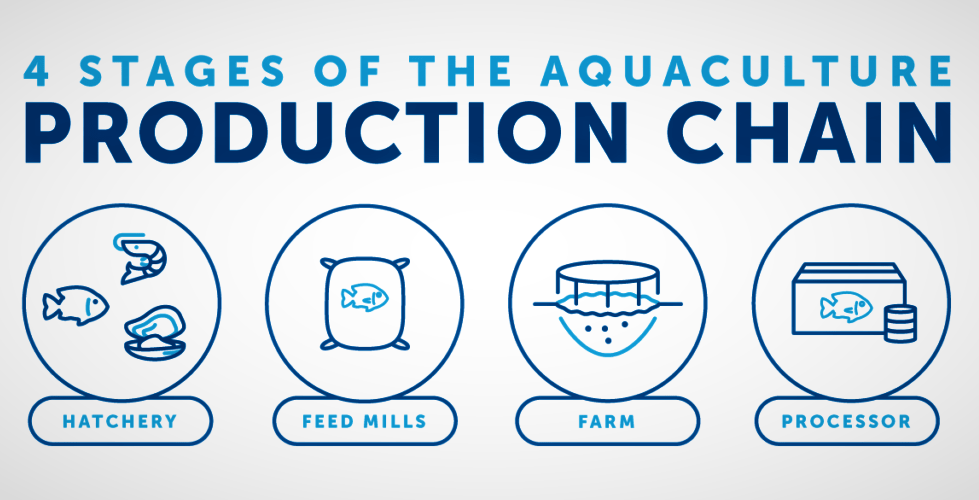
Methods of aquarium farming-to-table processing may vary by species. Typically, the construction chain has four stages, starting with the hatchery and ending at the seafood counter in your grocery store.
Every step is different in terms of its impact on the environment. The production quality and safety of the seafood noticed. This is why the Global Aquaculture Alliance conducts the Best Aquaculture Practices (BAP) third-party certification program.
There have been issues with these four aspects of aquaculture tanks in fish farms, and BAP seeks to improve the fish farming industry worldwide. This certification program covers every step of the supply chain of seafood products. You could be sure if your seafood were raised responsibly if it has the BAP logo.
The first phase of the aquaculture production chain is the hatchery. This is where fish breeding, hatching and fish rearing take place in the early stages of life. Once the animals are mature enough, they are transferred to the farm, which is the second aquaculture stage.
Here they grown to the size of a harvest, using feed produced at feed mills. The fishes then transported to a processing facility, packed and shipped to food retailers and grocery stores. That is the third step aquaculture mod.
Why Aquaculture Is Important?
Aquaculture has lower greenhouse gas emissions than other types of farming. Given what is aquaculture is all about, the abundance of fish in our oceans and other natural resources is constantly increasing every year. Humans need an alternative source of marine food to feed the earth’s growing population.

Unfortunately, the days of natural productivity of the ocean for the planet are rapidly decreasing. The annual catch of edible marine protein has already risen. The oceans cannot naturally meet the demand for seafood.
Positive Aquaculture Awareness:
Aquaculture is a tool to bridge the gap in the seafood supply.
Breeding fish responsibly and sustainably is a way to provide future generations with healthy and environmental friendly protein alternatives.
Not only is aquaculture necessary, but it is also a sustainable option for consumers, especially compared to other farm proteins.
Resource-efficient Food:
Seafood has the highest protein recognition just like chicken, pork and beef.
It also has the lowest feed growth ratio among similar forms of protein.



